What is a texture in OpenGL?
A texture is an OpenGL Object that contains one or more images that all have the same image format. A texture can be used in two ways: it can be the source of a texture access from a Shader, or it can be used as a render target.
What is Gl_repeat?
OpenGL offers 4 ways of handling this: GL_REPEAT : The integer part of the coordinate will be ignored and a repeating pattern is formed. GL_CLAMP_TO_EDGE : The coordinate will simply be clamped between 0 and 1 . GL_CLAMP_TO_BORDER : The coordinates that fall outside the range will be given a specified border color.
What is the OpenGL function used to generate an ID for the texture?
glTexImage2D The OpenGL function for loading image data from the computer’s memory into a 2D texture is glTexImage2D(), which takes the form: glTexImage2D(target, mipmapLevel, internalFormat, width, height, border, format, dataType, pixels); The target should be GL_TEXTURE_2D.
How are textures stored?
There are three kinds of storage for textures: mutable storage, immutable storage, and buffer storage. Only Buffer Textures can use buffer storage, where the texture gets its storage from a Buffer Object. And similarly, buffer textures cannot use mutable or immutable storage.
How do texture coordinates work?
Texture coordinates define how an image (or portion of an image) gets mapped to a geometry. A texture coordinate is associated with each vertex on the geometry, and it indicates what point within the texture image should be mapped to that vertex.
What is a texture name?
Texture object names are numbers that represent a specific texture. If you generate a texture object name, the system guarantees that it will uniquely identify that specific texture within that OpenGL context, until you delete the texture (and likely sometime thereafter).
What is a texture sampler?
A sampler is a set of GLSL variable types. Variables of one of the sampler types must be uniforms or as function parameters. Each sampler in a program represents a single texture of a particular texture type. The type of the sampler corresponds to the type of the texture that can be used by that sampler.
What is a texture coordinate?
What is Bindless texture?
Bindless Textures are a method for having Shaders use a Texture by an integer number rather than by binding them to the OpenGL Context. These texture can be used by samplers or images.
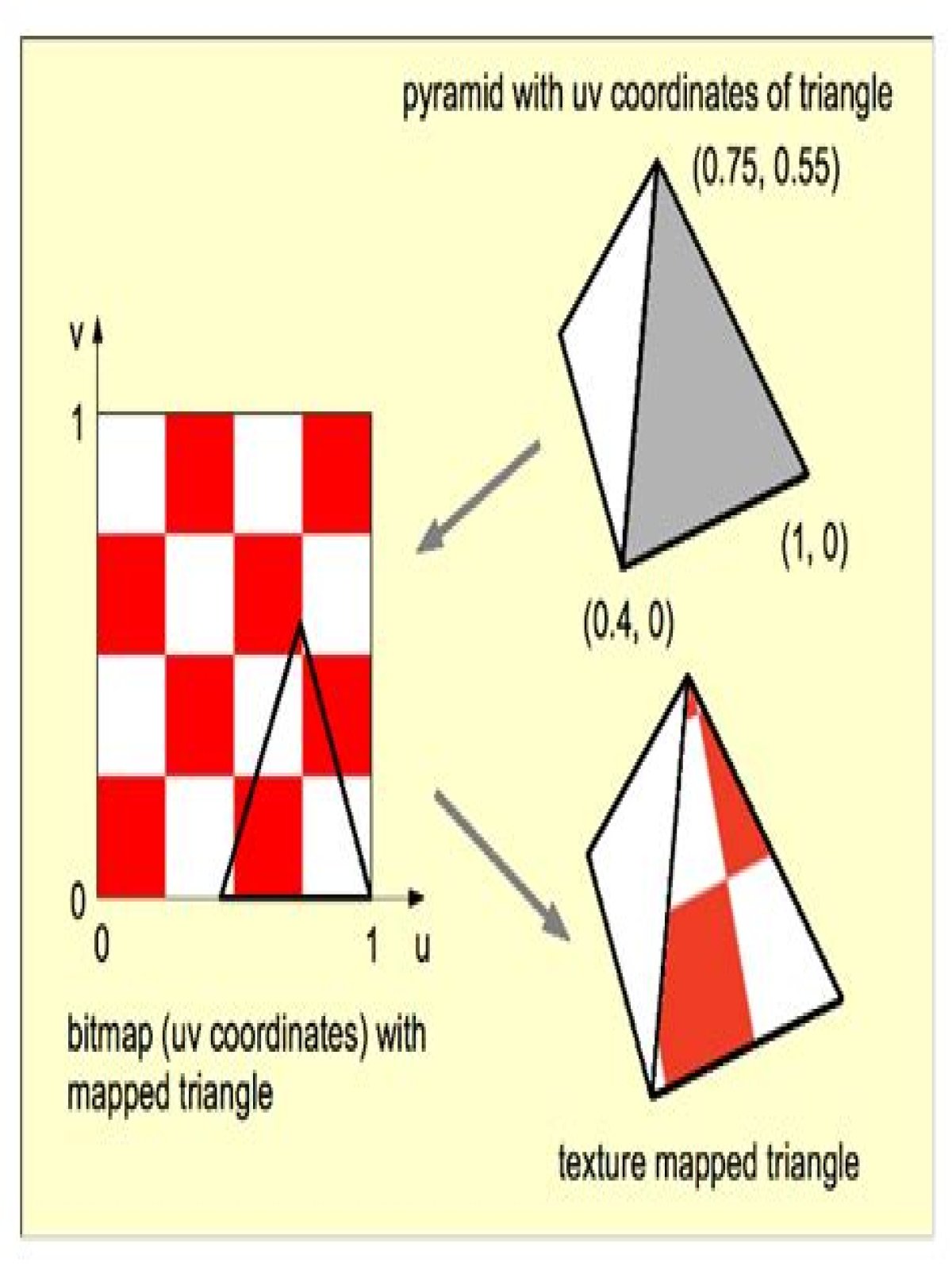
What is UV OpenGL?
About UV coordinates When texturing a mesh, you need a way to tell to OpenGL which part of the image has to be used for each triangle. This is done with UV coordinates. These coordinates are used to access the texture, in the following way : Notice how the texture is distorted on the triangle.
What is the relationship between texture coordinates and resolution in OpenGL?
Texture coordinates do not depend on resolution but can be any floating point value, thus OpenGL has to figure out which texture pixel (also known as a texel) to map the texture coordinate to. This becomes especially important if you have a very large object and a low resolution texture.
What is GL_nearest in OpenGL?
GL_NEAREST (also known as nearest neighbor or point filtering) is the default texture filtering method of OpenGL. When set to GL_NEAREST, OpenGL selects the texel that center is closest to the texture coordinate. Below you can see 4 pixels where the cross represents the exact texture coordinate.
How do you filter a texture in OpenGL?
Texture Filtering. GL_NEAREST (also known as nearest neighbor filtering) is the default texture filtering method of OpenGL. When set to GL_NEAREST, OpenGL selects the pixel which center is closest to the texture coordinate. Below you can see 4 pixels where the cross represents the exact texture coordinate.
How many texture units can I use with OpenGL?
OpenGL should have a at least a minimum of 16 texture units for you to use which you can activate using GL_TEXTURE0 to GL_TEXTURE15. They are defined in order so we could also get GL_TEXTURE8 via GL_TEXTURE0 + 8 for example, which is useful when we’d have to loop over several texture units.