What do Lab color values mean?
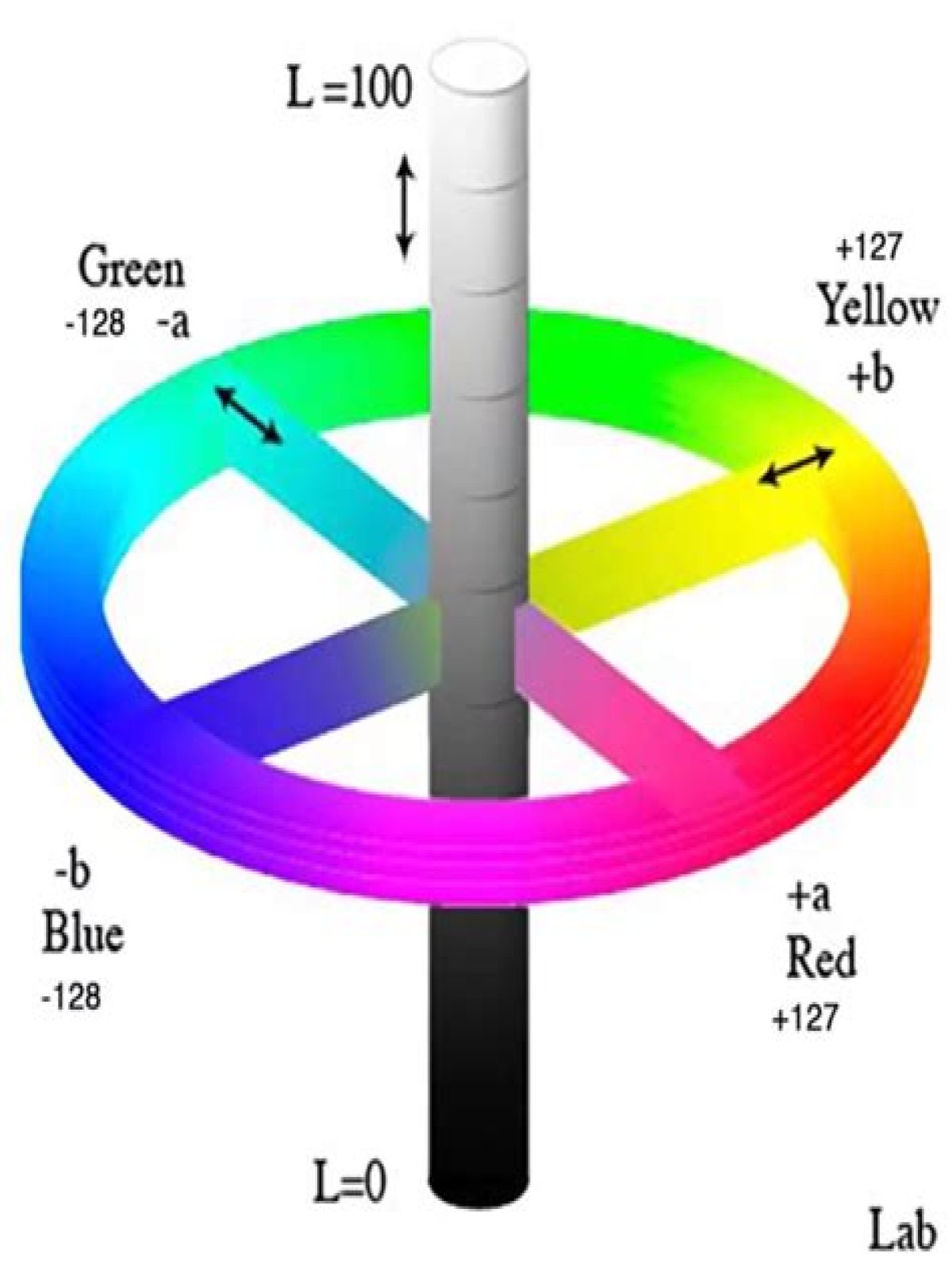
Lab Color is a more accurate color space. It uses three values (L, a, and b) to specify colors. The a-axis (green to red), b-axis (blue to yellow) and Lightness axis. The best thing about Lab Color is that it’s device-independent. That means that it’s easier to achieve exactly the same color across different media.
How do you read lab colors?
A color measurement movement in the +a direction depicts a shift toward red. Along the b* axis, +b movement represents a shift toward yellow. The center L* axis shows L = 0 (black or total absorption) at the bottom. At the center of this plane is neutral or gray.
What does red mean in a lab?
It screens for anemia or other blood disorders and can detect infections. What’s considered normal: Red blood cells (RBC): Between 4.32 and 5.72 trillion cells/liter for men. Between 3.90 and 5.03 trillion cells/liter for women.
What is the characteristic of CIE L * a * b * color space?
CIELAB or CIE L*a*b* is a device-independent, 3D color space that enables accurate measurement and comparison of all perceivable colors using three color values. In this color space, numerical differences between values roughly correspond to the amount of change humans see between colors.
How is color strength measured?
In order to measure the strength of a color, we use a machine called an absorbance spectrophotometer. The machine shines light through a cell containing a colorant solution and then measures the amount of light that is able to pass through the sample as compared to the original amount of light from the source.
What does Delta E indicate in the CIE L * a * b * color space?
Delta E* (Total Color Difference) is calculated based on delta L*, a*, b* color differences and represents the distance of a line between the sample and standard.
What is a good Delta E value?
If a Delta E number is less than 1 between two colors that are not touching, it is barely perceivable by the average human observer. A Delta E between 3 and 6 is usually considered an acceptable number in commercial reproduction, but the color difference may be perceived by printing and graphic professionals.
Is Delta E 2 GOOD?
The average person won’t notice a Delta E error that’s less than 3. However, the trained eye can see down to errors of 1, while errors less than 1 are usually considered imperceptible. Top monitors achieve a Delta E of 2, where the color difference is barely detectable.
What are L*A*B* color values?
Like geographic coordinates – longitude, latitude, and altitude – L*a*b* color values give us a way to locate and communicate colors. What’s the history of L*a*b*? In the 1940’s, Richard Hunter introduced a tri-stimulus model, Lab, which is scaled to achieve near uniform spacing of perceived color differences.
What is the Hunter L A B color scale?
The Hunter L, a, b color scale can be used on any object whose color may be measured. It is not used as frequently today as it was in the past because the CIE L*a*b* scale, which was released in 1976, has gained popularity.
What is the difference between L*A*B* and L*C*H?
The L*C*h color space is similar to L*a*b*, but it describes color differently using cylindrical coordinates instead of rectangular coordinates. In this color space, L* indicates lightness, C* represents chroma, and h is the hue angle. Chroma and hue are calculated from the a* and b* coordinates in L*a*b*.
What does L* mean in color space?
In this color space, L* indicates lightness, C* represents chroma, and h is the hue angle. Chroma and hue are calculated from the a* and b* coordinates in L*a*b*.